

报告题目:Excellent Catalytic Activity of a Pd-promoted MnOx Catalyst for Purifying Automotive Exhaust Gases – Reduction of precious metal use
报告时间:2020年09月23日(星期三)上午10:00-11:30
报告地点:腾讯会议
会议ID: 558083645
报 告 人:Prof. Tsunehiro Tanaka教授(田中庸裕,日本京都大学)
报告摘要:
activity and reduced precious metal use. Such catalysts must undergo simultaneous CO/ hydrocarbon oxidations and NO reduction. A Pd catalyst supported on Mn-modified hexagonal YbFeO3 (Pd/Mn-YFO) exhibited extremely high activity at low temperature via a Mars-van Krevelen (MvK) mechanism involving lattice oxygen and oxygen vacancy site in the catalyst support.
CO + OL → CO2 + VO
NO + VO → Ns + OL
Ns + Ns → N2
where OL is a lattice oxygen, VO is an oxygen vacancy site, and Ns is a dissociated N species formed on the surface of the MnO-like species.
NO reduction proceeded by high CO and C3H6 oxidation activity of Pd/Mn-YFO, and the catalytic activity of 1.0 wt% Pd/Mn-YFO was higher than that of 5.0 wt% Pd/Al2O3, despite the lower Pd loading. We clarified that the lattice oxygen in MnOx, which existed on the surface of YFO, consumed by CO and C3H6 oxidation was recovered by NO to form N2 via MvK-type NO reduction, while the Pd species promoted NO adsorption and dissociation on MnO-like species.
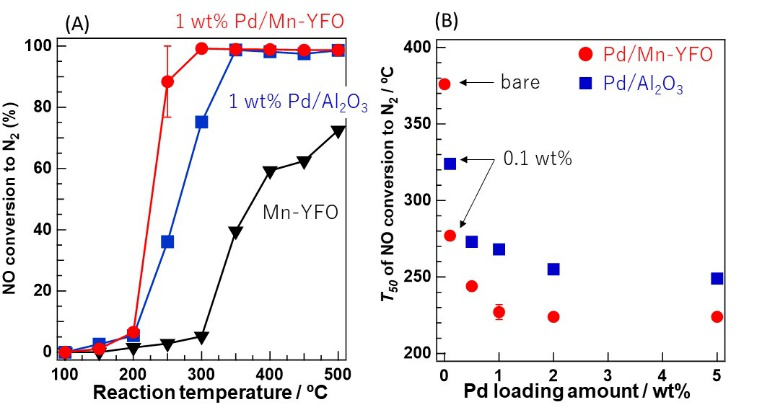
Figure (A) NO conversions and (B) T50 values for NO reduction with CO and C3H6 over the Pd catalysts. The reaction gas comprised 1000 ppm NO, 1000 ppm CO, 250 ppm C3H6, and 1125 ppm O2 with He as the balance. T50 was defined as the temperature at which 50% catalytic activity was achieved.
References:
S. Hosokawa, S. Matsumoto, K. Onishi, H. Asakura, K. Teramura, T. Tanaka, Catal. Today,2019, 332, 183-188.
S. Hosokawa, R. Tada, T. Shibano, S. Matsumoto, K. Teramura, T. Tanaka, Catal. Sci. Technol.,2016, 6, 7868-7874.
S. Hosokawa, T. Shibano, H. Koga, M. Matsui, H. Asakura, K. Teramura, M. Okumura, T. Tanaka
ChemCatChem, 2020, in press.

报告人简介:
Tsunehiro Tanaka教授,现任日本京都大学工程学院分子工程系教授,1987年于日本京都大学化学专业获得博士学位,1987-1990年在美国北海道大学化学系(Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University)做助理教授,1990年进入日本京都大学工程学院工作。1996年在中国兰州物理化学研究所担任客座教授。1996年在意大利都灵大学物理无机材料化学系担任客座学者。目前担任日本京都大学催化剂与电池元素战略计划主任,英国皇家学会《Catalysis Science & Technology》副主编。曾获得“日本催化协会青年科学家奖”。目前主要从事多相光催化研究;机动车催化剂元素战略研发;催化反应表征研究等。